61 million people in India have osteoporosis & out of these, 80 percent are women
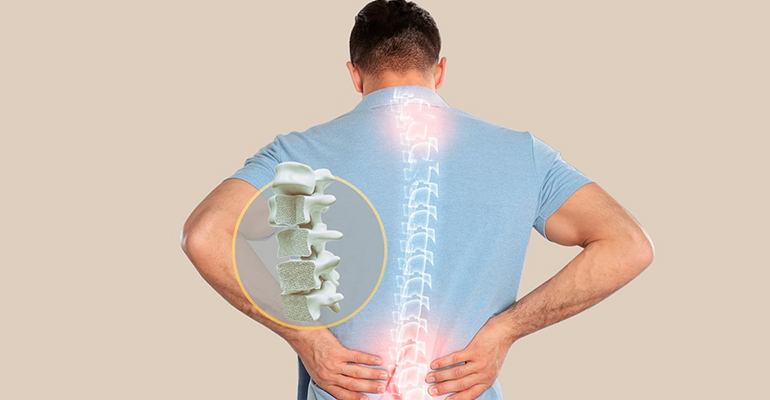
Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become weak and brittle due to a decrease in bone density and quality. In healthy bones, a process called bone remodeling ensures that old bone tissue is broken down and replaced with new tissue. However, with osteoporosis, this process is disrupted, leading to a loss of bone mass. The bones become porous and fragile, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in the spine, hip, and wrist. While it is more common in postmenopausal women, osteoporosis can affect both men and women at any age.
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it progresses without obvious symptoms until a fracture occurs. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments can help you take proactive steps to protect your bone health.
This can result from fractured or collapsed vertebrae.

A noticeable decrease in height may occur as the vertebrae compress.
A curvature in the spine, often called a "dowager’s hump," can develop.

Fragile bones are more prone to fractures, which can occur from minor falls or even simple movements like bending or coughing.
There are mainly four types of Osteoporosis, Osteoporosis in Elderly, Osteoporosis in Post Menopausal Female, Vitamin D Deficiency & Parathyroid Disorder
Osteoporosis in the elderly is a common condition where bone density decreases with age, leading to fragile bones and an increased risk of fractures. This occurs due to slower bone regeneration, reduced calcium absorption, and hormonal changes in both men and women. Hip, spine, and wrist fractures are most common in older adults. Factors like inactivity, poor nutrition, and chronic illnesses exacerbate the condition. Regular weight-bearing exercises, calcium-rich diets, and medications can help manage osteoporosis in the elderly.
Postmenopausal women are at a higher risk of osteoporosis due to decreased estrogen levels, a hormone essential for maintaining bone density. Rapid bone loss typically occurs within the first 5-10 years after menopause, making fractures in the spine, hip, and wrist more likely. Additional risk factors include family history, low body weight, and smoking. Treatment involves calcium and vitamin D supplements, hormone replacement therapy, and medications like bisphosphonates to slow bone loss and prevent fractures.
Vitamin D is critical for calcium absorption and bone health. A deficiency leads to weakened bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Factors such as limited sunlight exposure, poor dietary intake, or malabsorption conditions can cause this deficiency. Symptoms may include bone pain, muscle weakness, and frequent fractures. Treatment involves restoring vitamin D levels through supplements, dietary changes, and safe sun exposure, along with calcium intake to improve bone density and strength.
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates calcium levels in the body. Overactivity of the parathyroid glands (hyperparathyroidism) can lead to excessive calcium being removed from bones, causing osteoporosis. This results in weakened bones, frequent fractures, and even kidney stones due to high calcium levels in the blood. Diagnosis involves blood tests and imaging studies. Treatment may include parathyroid surgery, medications, and lifestyle adjustments to restore calcium balance and prevent further bone loss.
we help in managing and treating osteoporosis, helping patients maintain bone health and prevent fractures. Treatment typically includes a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and ongoing monitoring.
The primary medications used to treat osteoporosis are bisphosphonates, which slow the breakdown of bone. Other options include hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can help maintain bone density, especially in postmenopausal women. Additionally, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), denosumab, and teriparatide are medications that may be prescribed based on individual patient needs.
Ensuring an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone health. Calcium is the building block of bones, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium effectively.
Incorporating weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, or resistance training helps strengthen bones. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is also essential for maintaining bone health.
Since fractures are the most serious consequence of osteoporosis, minimizing the risk of falls is crucial. We offer guidance on how to improve balance, posture, and strength to reduce the likelihood of falling.
WhatsApp us
