1 out of every 10 adults in India has Diabetes and one in every third household has diabetic patients
Diabetes has become a very common issue these days which may affect people regardless of their age. It develops when your pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin or any at all, or when your body isn’t responding to the effects of insulin properly.

You might very often feel that your mouth is dry and you need to drink water.

You might get the feeling to drink more water than usual to satisfy your thirst.
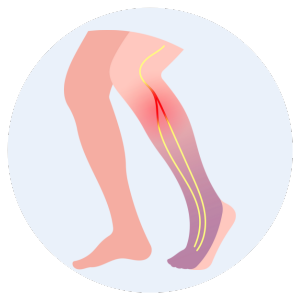
Your feet will sometimes start tingling or it may get numb for sometime.

Your vision or sight may be blurry due to diabetes.

Incase you get any cuts in your body, it will take more time than general to be healed.

You may got a lot of frequent infections like gum infections or maybe vaginal infections if you are a woman.
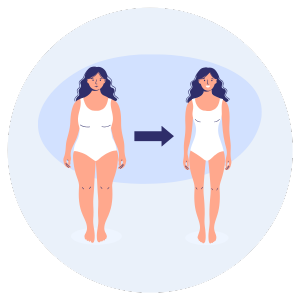
You might see that you are losing weight without doing anything at all.
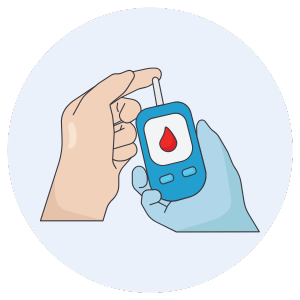
You may have a high blood sugar levels but no noticeable symptoms
There are mainly three types of diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes and Type 1 Diabetes & Other types of Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes mainly affects the adults but children can be also prone to it. It is a condition in which your own body cells do not respond to the insulin. It can also occur when your body is not making enough insulin.
Type 1 Diabetes mainly affects the children and adults of young age but it may affect anyone of any age. In this type, our own immune system starts attacking the insulin-producing cells located in the pancreas of our body.
Early aggressive treatment with an emphases on lifestyle measures can help reduce the risk of long term health complications.
WhatsApp us
